Dengue an infection places in subzones over weeks
All dengue clusters are recorded in 21 weeks from 15 February to 9 July, which covers the nationwide lockdown interval from 7 April to 1 June. The dataset of those 21 weeks is thus categorised into three elements, particularly earlier than lockdown (BL), CB, and after lockdown (AL) respectively.
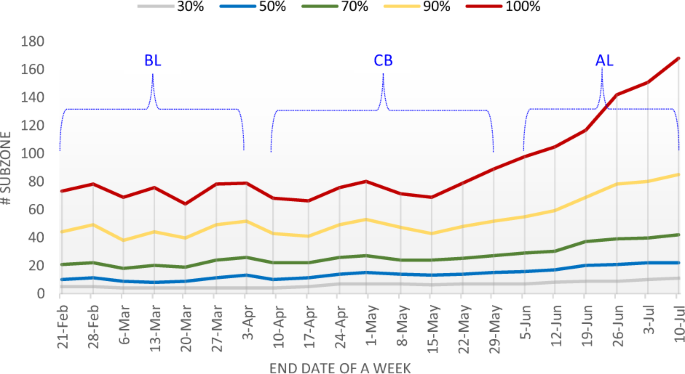
For every week, we first rank the subzones in a descending order when it comes to the variety of places contained in the subzone in that week. Then we rely the variety of top-ranked subzones with cumulatively no fewer than a sure share of all of the places. The outcomes are proven in Fig. 3. As could be noticed, when the share is ready to be 100%, that means that every one places are taken under consideration, there was a major enhance within the subzone quantity beginning within the second half of Could. This means that the dengue transmission places had been dispersed to extra subzones which had been initially freed from dengue clusters. It’s attention-grabbing to watch that this dispersion began earlier than lockdown formally got here to an finish. The explanations resulting in it might want some additional investigation.
Additional observations present that, when the cumulative share is respectively set as 30%, 50%, and 70%, the corresponding subzone numbers stay comparatively steady at low values. It implies that, for many of time, a small variety of subzones (fewer than 30 subzones earlier than 19 June) contained no fewer than 70% of all of the dengue an infection places. Even when the share worth is ready to be 90%, although the subzone quantity began to extend in Could, it stored as being lower than 85 in all weeks. Solely when the share is ready as 100%, a considerably bigger variety of subzones are enrolled beginning in Could. These newly enrolled subzones, mixed collectively, include not more than 10% of all of the dengue an infection places. Take a selected week from 16 Could to 22 Could for instance, 90% of all places had been reported in 48 subzones, whereas the opposite 10% of places are scattered in 31 subzones. Observe that within the final two weeks of Could, the variety of the enrolled subzones elevated whereas the variety of reported an infection places nonetheless remained largely steady. When it got here to June and July of 2020, nevertheless, the variety of enrolled subzones additional elevated, accompanied with a major enhance within the variety of infecting places.
An infection location quantity modifications in subzones throughout lockdown
By trying into the time sequence of location quantity in every subzone, some particulars of the situation quantity modifications within the three durations (BL, CB, and AL respectively) might be noticed. Particularly, given a subzone z, the common location quantity, loci, j, in every interval is calculated as
$${A}_{z}^{BL}=frac{1}{{n}^{BL}}{sum }_{i=z,jin BL}lo{c}_{i,j}$$
$${A}_{z}^{CB}=frac{1}{{n}^{CB}}{sum }_{i=z,jin CB}lo{c}_{i,j}$$
$${A}_{z}^{AL}=frac{1}{{n}^{AL}}{sum }_{i=z,jin AL}lo{c}_{i,j}$$
the place i is the subzone ID of the situation document within the dataset and j is the top date of the week within the knowledge document. nBL, nCB, and nAL are respectively the variety of weeks for every interval (BL, CB, and AL). Wanting into the time sequence, two several types of modifications could be noticed in several subzones, that are respectively outlined as follows.
-
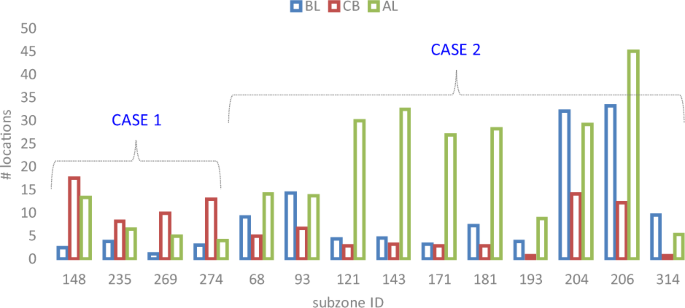
CASE 1: the variety of location quantity, that are concerned within the dengue clusters, elevated throughout the nationwide lockdown and it subsequently decreased after the lockdown.
-
CASE 2: the situation quantity sharply decreased throughout the lockdown and rose again after the lockdown.
We’ve that ({A}_{z}^{BL} < {A}_{z}^{CB} > {A}_{z}^{AL}) for CASE 1 and ({A}_{z}^{BL} > {A}_{z}^{CB} < {A}_{z}^{AL}) for CASE 2.
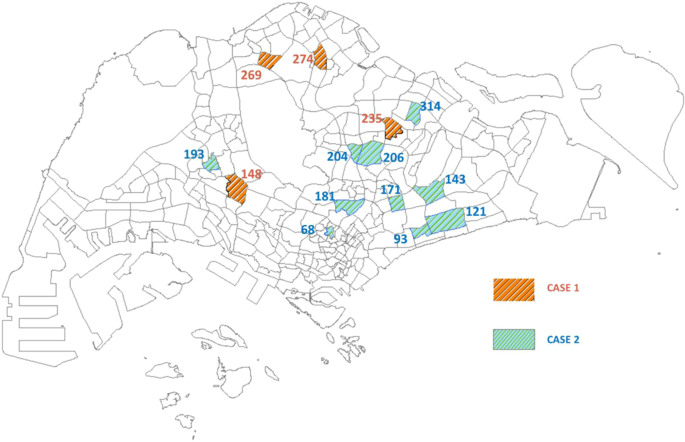
The time sequence of those two particular circumstances could assist anchor which areas in Singapore have been probably influenced by the lockdown when it comes to the reported location. The subzones for the 2 totally different circumstances are proven in Fig. 4. The corresponding geographical places of those subzones for CASE 1 and CASE 2 are illustrated in Fig. 5.