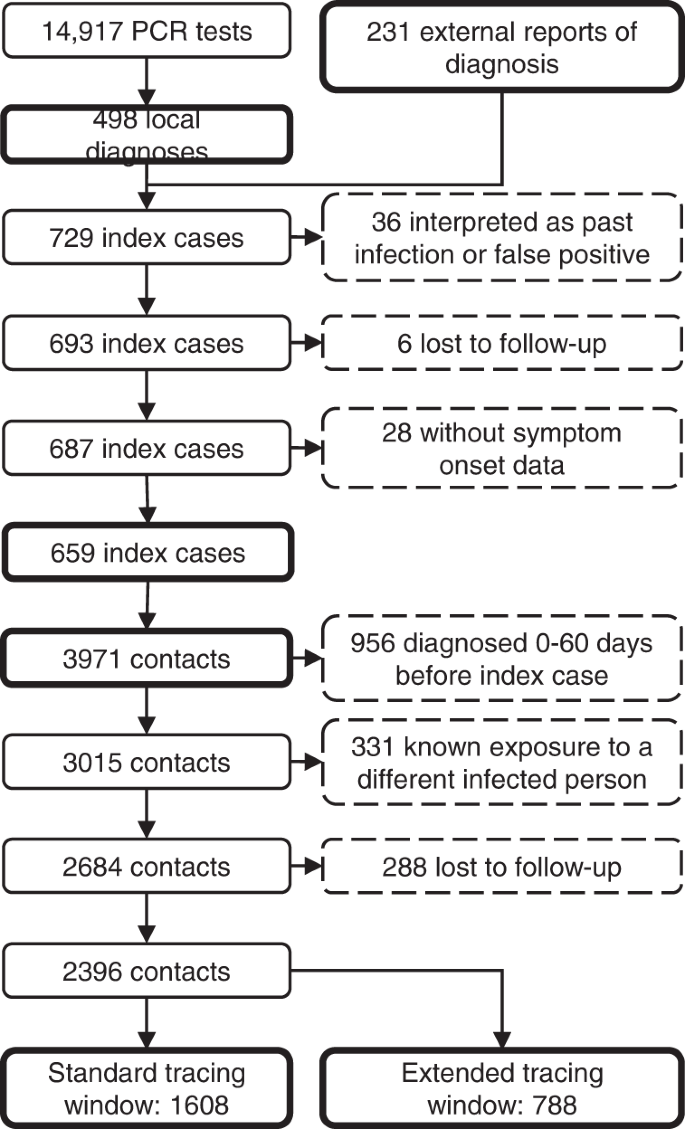
Examine circumstances and contacts
Our take a look at and hint programme ran from September 2020 till Could 2022. Resulting from gradual enhancements in organisation and information assortment, there was a marked enhance within the ratio of contacts with end result information after the preliminary months of the programme (Supplementary Fig. 3). The research interval for the principle analyses was chosen from 1st February 2021 to thirty first Could 2021, which was after the preliminary set-up section of the programme and included each an upward and a downward pattern in country-wide an infection charges.
In complete, 14,917 college students underwent RT-qPCR testing at our centre on this interval (3.8 assessments per 1000 individuals each day), leading to 498 college students with a brand new prognosis of COVID-19. An additional 231 optimistic RT-qPCR take a look at outcomes of scholars within the research inhabitants have been reported to us from exterior sources, leading to a complete of 729 circumstances. Thirty-six (4.9%) of those have been interpreted as a previous an infection or false optimistic by the treating doctor, leaving 693 precise circumstances (14-day incidence of 245 per 100,000). Six circumstances (0.9%) have been thought-about misplaced to follow-up, as a result of they might by no means be contacted by the contact tracing staff, and 28 (4.1%) have been excluded as a result of information on presence of signs was lacking. Subsequently, 659 index circumstances remained within the evaluation (Fig. 3).
In complete, 72.5% of index circumstances self-reported being symptomatic on the time of testing, which was just like the nationwide common37. Index circumstances had a imply age of 21.4 years (SD: 3.60 years, lacking information 15.0%) and have been 51.1% male (lacking information 12.1%).
Contact tracing of the index circumstances resulted in 3971 case-contact pairs (imply 6.0 contacts per case, 2.2 instances the nationwide common37), of which 956 (24.1%) have been excluded as a result of the contact particular person already had a optimistic take a look at consequence 0 to 60 days earlier than the optimistic take a look at of the index case. One other 331 (11.0%) contacts have been excluded as a result of they already had a identified publicity to a special contaminated particular person inside 7 days earlier than the tracing interview. Lastly, 288 contacts (10.7%) have been misplaced to follow-up. The distribution of the variety of contacts per index case in proven in Supplementary Fig. 4.
The ensuing 2396 contacts have been divided into two teams. The usual tracing window group, which might have been recognized by means of normal apply, consisted of 1608 people in shut contact with the index case within the interval from 2 days earlier than onset or take a look at till the contact tracing interview. The backward traced group consisted of 788 extra contacts within the prolonged tracing window, i.e. their final shut interplay with the index case was 3 to 7 days earlier than onset or take a look at. For the principle evaluation, we didn’t make assumptions on the directionality of transmission. Subsequently, each the ahead and backward traced group possible included guardian, sibling and youngster circumstances.
We didn’t gather demographic information on contacts of index circumstances.
The management group consisted of all 1461 college students who attended our take a look at centre for the primary time with self-reported signs suggestive of COVID-19 as the principle cause for his or her take a look at.
There was a barely greater proportion of girls within the management group (56.5%, lacking information 3.0%) in comparison with the index circumstances, whereas the imply age was comparable (22.0 years; SD 3.84 years, lacking information 3.0%). The temporal distribution of people within the backward traced contact and symptomatic management teams is proven in Supplementary Fig. 1a.
Excessive threat of an infection within the prolonged tracing window
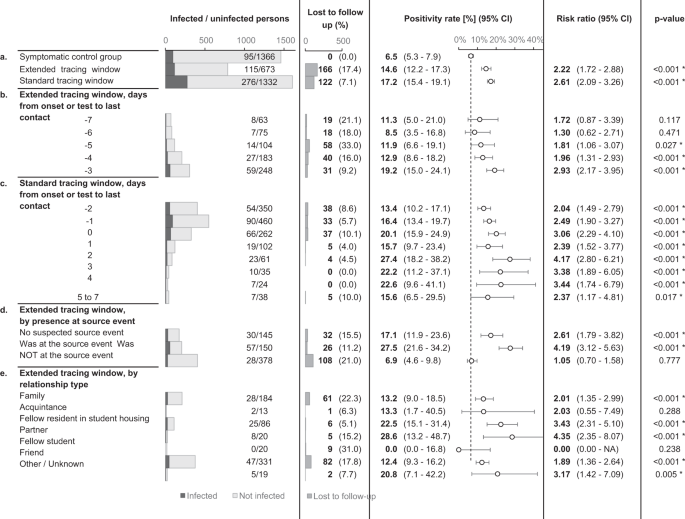
By extending the contact tracing window, 49% extra contacts in danger and 42% extra circumstances have been recognized as direct contacts of an index case, in comparison with normal contact tracing apply alone.
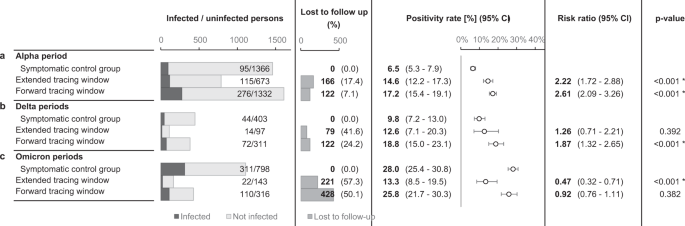
The chance of an infection in the usual and prolonged tracing window teams was comparable, particularly 17.2% within the former (CI 15.4–19.1%) and 14.6% within the latter (CI 12.2–17.3%). The chance within the prolonged tracing window group was considerably greater (threat ratio 2.22, CI 1.72–2.88, p < 0.0001) than the chance of 6.5% (CI 5.3–7.9%) within the management group, demonstrating the relative effectivity of extending the contact tracing window to 7 days previous to symptom onset or take a look at (Fig. 4).
The dotted line signifies the positivity fee within the management group. The error bars point out 95% two-sided confidence intervals (Clopper–Pearson). * signifies a statistically important distinction compared to the management group (p < 0.05) as assessed utilizing a two-sided Chi-squared take a look at, not adjusted for a number of comparisons. Part a assessments the principle speculation by evaluating the prolonged tracing window to the symptomatic management group. Subgroups by the numbers of days from onset or take a look at of the index case to the final interplay with the index case are proven in part b, c for the prolonged and normal tracing home windows respectively. Part d exhibits subgroups in accordance with presence at suspected supply occasions, and subgroups by relationship sort are proven in e.
Contacts in the usual and prolonged tracing window teams have been subgrouped by their final day of contact with the index case, relative to symptom onset or take a look at. The outcomes present that the variety of extra recognized shut contacts per day decreased markedly because the tracing window was prolonged backward. The chance of an infection different from 8.5 to 19.2%, and the arrogance interval decrease certain didn’t drop under 3.5% for any of those subgroups within the prolonged tracing window. For day 3, 4 and 5 earlier than onset or take a look at, the chance was considerably greater than the management group (p < 0.05).
The chance shouldn’t be restricted to suspected supply occasions
An essential consideration when deciding between a supply investigation method and an prolonged tracing window is the chance of an infection for contacts not current at suspected supply occasions. A suspected supply occasion was recognized for 80.6% of index circumstances. If the contact tracing interview did not recommend a supply occasion, the chance of an infection for prolonged tracing window contacts was 17.1% (CI 11.9–23.6%). If a supply occasion was recognized, the chance was round 4 instances greater for contacts who attended the occasion (absolute threat 27.5%, CI 21.6–34.2%) in comparison with those that didn’t. The latter group nonetheless had a threat of 6.9% (CI 4.6–9.8%), which was just like the symptomatic management group however not considerably greater (Fig. 4a).
Danger by relationship sort
In an explorative subgroup evaluation, prolonged tracing window contacts have been grouped in accordance with relationship sort with the index case. The vast majority of recognized contacts have been both household (28.6%), fellow residents in pupil housing (12.3%), or mates (48.2%). Every of those three teams had a considerably elevated an infection threat as in comparison with the symptomatic management group. The opposite subgroups lacked adequate numbers for statistical energy (Fig. 4e).
Backward contact tracing identifies circumstances later of their an infection
Efficient contact tracing requires the detection of contaminated contacts as quickly as doable, earlier than they attain the tip of their contagious interval. The sibling and particularly guardian circumstances focused by backward contact tracing may be anticipated to be in a later stage of an infection in comparison with ahead traced contacts, probably resulting in decrease effectivity of tracing, testing and quarantine measures.
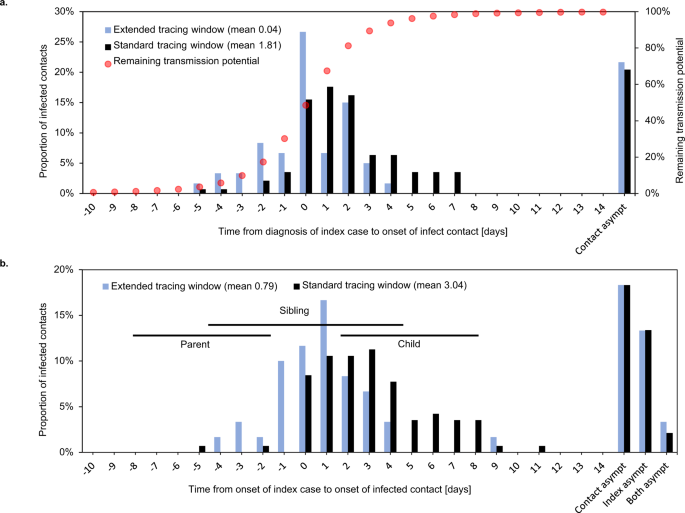
Certainly, when evaluating the date of detection of an index case with the onset date of their contaminated contact, the contaminated contacts within the prolonged tracing window have been on common 1.8 days later of their infectious cycle in comparison with these in the usual tracing window (Fig. 5a). The distinction might be interpreted as a discount in touch tracing effectivity equal to a further testing or tracing delay of the identical interval.
Symptom onset in contaminated contacts relative to sampling (a) or symptom onset (b) of the index case. Asympt asymptomatic. Case–contact pairs that have been excluded from the imply calculation as a result of both or each have been asymptomatic, are proven on the appropriate. Panel a exhibits the delay between detection of an index case and symptom onset of their contaminated contact. Crimson dots present the estimated remaining fraction of transmission potential of the contaminated contact on the time of sampling of the index case. Ahead traced symptomatic contacts have been detected on common 1.8 days earlier of their infectious cycle than their backward traced counterparts, assuming equal delays between index case prognosis and tracing of the contact. This resulted in a 28% decrease imply remaining transmission potential for backward traced contacts on the time of index case testing. Panel b exhibits the delay between symptom onset of an index case and their contaminated contact. Horizontal traces point out the twenty fifth–seventy fifth percentile ranges of anticipated timings for guardian, sibling and youngster circumstances, based mostly on a printed regular distribution of the serial interval38. The noticed timings are suitable with a excessive proportion of sibling circumstances and few guardian or youngster circumstances within the backward traced group.
The distinction of 1.8 days in touch symptom onset relative to index case detection is far smaller than we might count on if all back and forth traced contacts have been guardian and youngster circumstances, respectively (double the imply serial interval of round 5 days)38. One doable rationalization is than sibling circumstances make up a substantial share of contacts in each teams. Though we can’t verify the relative positions of contaminated contacts within the transmission tree, the noticed timings can be in keeping with the next fraction of sibling circumstances within the backward traced group and a minority of guardian circumstances in each teams (Fig. 5b).
To quantify the fraction of transmissions averted by means of quarantine of symptomatic contaminated contacts, we used a distribution of timing of transmission relative to symptom onset (Fig. 5a)39. On the time of testing of the index case, the imply fraction of remaining transmission potential was 28% decrease for contaminated backward versus ahead traced contacts.
Much less assessments and shorter quarantine within the backward traced group
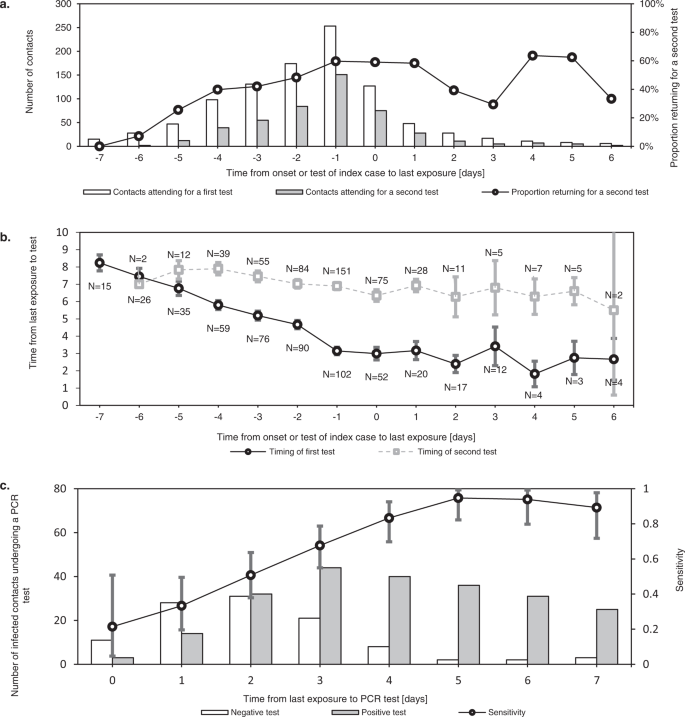
The worth of contact testing relies upon not solely on take a look at particular diagnostic efficiency, but additionally on timing. Fast testing after contact identification can speed up iterative tracing (“take a look at to hint”). It will possibly additionally cut back the entire length spent in quarantine and isolation, in settings the place launch from isolation depends on the timing of prognosis. Assessments after a latent interval are extra delicate and might thus be used to permit shortening of quarantine for non-infected contacts (“take a look at to launch”) (Fig. 6c)40.
Error bars point out 95% confidence intervals. a exhibits the variety of contacts who underwent a primary and second assessments at our take a look at centre after their publicity. This demonstrates how testing instantly after publicity (“take a look at to hint”) was most frequently complemented with testing after a latent interval (“take a look at to launch”). Whereas the previous primarily helps iterative tracing and in some circumstances a shortened isolation interval, the latter permits shortening of quarantine for non-infected contacts. Because the delay between final publicity and symptom onset or testing of the index case elevated, the proportion of contacts requiring two assessments decreased. b exhibits the imply timing of first and seconds assessments at our centre for contacts, relative to their final publicity. The distinction in timing of the primary and second assessments is lowered because the contact tracing window is prolonged additional again in time. c exhibits the take a look at outcomes of contaminated contacts by day after final publicity, demonstrating how the sensitivity of RT-qPCR testing elevated quickly within the first days after publicity.
In the course of the research interval, contacts have been requested to bear RT-qPCR assessments each as quickly as doable after identification and once more 7 days after final publicity, which is mirrored within the timing of contact testing in our dataset (Fig. 6b).
As backward traced contacts have been detected a minimal of three days after their final publicity by definition and a mean of 4.0 days longer after final publicity than ahead traced contacts in our dataset, a single take a look at at identification was extra prone to serve each a “take a look at to hint” and “take a look at to launch” technique concurrently. We estimate a discount of 17% within the variety of assessments required per traced contact, based mostly on a delay from index case testing to contact testing of 1 day (Supplementary Fig. 5).
One other consequence of this inherent distinction in final publicity date is that, in our dataset, the imply length of quarantine was 3.0 days (57%) shorter for contacts within the backward traced group in comparison with the ahead traced group. This consequence assumes a length of quarantine from index case prognosis till 7 days after publicity, with a minimal of 1 day to permit for contact testing (Supplementary Fig. 5).
Affect of fixing viral variants
Consecutive SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOC) might have challenged the effectiveness of contact tracing in a number of methods. First, elevated intrinsic transmissibility might have quickly overwhelmed the general public well being system41,42. Second, shortened incubation durations and serial intervals presumably outpaced the delays inherent in testing and tracing34,43,44. To evaluate the affect of those altered transmission dynamics, the principle evaluation was repeated for durations when the Delta and Omicrons VOCs have been dominant nationally (Fig. 7). These durations differed from the principle research interval not solely when it comes to the dominant circulating VOC, but additionally within the immune standing of the goal inhabitants, the final contact restrictions in place, the COVID-19 incidence fee and the federal government necessities regarding testing and quarantine (Supplementary Figs. 3, 7, 9 and 10)37,45,46.
The contact befell in chosen durations, differing as regards to the dominant variants of concern, immunity, degree of viral circulation, social contact restrictions and authorities testing/quarantine technique. The error bars point out 95% two-sided confidence intervals (Clopper–Pearson). * signifies a statistically important distinction compared to the management group (p < 0.05) as assessed utilizing a two-sided Chi-squared take a look at, not adjusted for a number of comparisons. a repeats the principle research outcomes from Fig. 4a, whereas the outcomes from subsequent durations are proven in b, c.
Sadly, follow-up charges dropped markedly after the principle research interval, particularly for contacts within the prolonged tracing window. In the course of the durations characterised by Delta dominance, backward traced contacts had comparable PR to each ahead traced contacts and symptomatic controls, additional supporting our primary speculation (Fig. 7b). In the course of the durations characterised by Omicron dominance and an nearly absolutely vaccinated inhabitants, backward traced contacts retained a really excessive PR (imply 13.3%, CI 8.5–19.5%)47,48. It was nonetheless considerably decrease than the a lot elevated PR in symptomatic controls and ahead traced contacts (Fig. 7c).
Iterative contact tracing in a branching course of mannequin
As talked about, iterative contact tracing of contaminated contacts is assumed to play a bigger function in backward contact tracing. Nonetheless, most of the reported contacts in our dataset have been outdoors the research inhabitants, which suggests their contacts weren’t iteratively traced utilizing the identical backward tracing technique if contaminated. To estimate how environment friendly backward contact tracing can be if all contaminated contacts have been iteratively traced, we used a easy branching course of mannequin. The design of the mannequin, described in Supplementary Strategies, requires no assumptions on the course of transmission or the chance of an contaminated contact being traced. This mannequin allowed us to estimate, for our setting, the entire anticipated variety of traced contacts from a major index case, over a number of iterations of contact tracing, based mostly on the noticed numbers of contaminated contacts in the principle research interval (Supplementary Fig. 8 and Supplementary Desk 1). We then quantified a number of measures of prices and advantages of an prolonged contact tracing window relative to plain contact tracing apply alone.
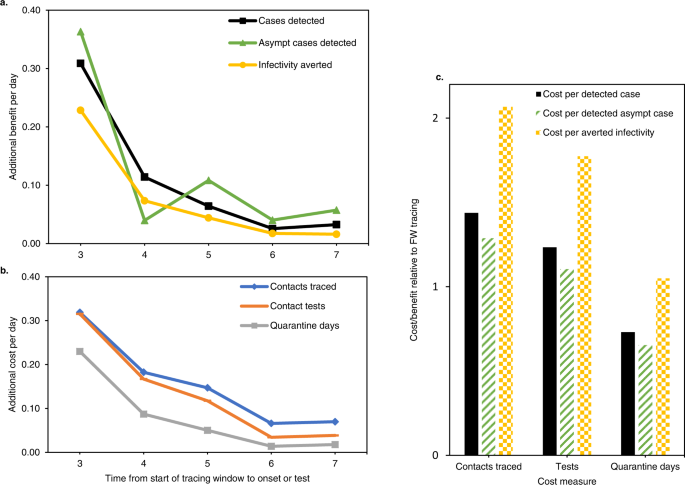
The outcomes are summarised in Fig. 8 and mannequin particulars are proven in Supplementary Fig. 8. When bearing in mind iterative tracing of back and forth traced contacts, an prolonged contact tracing window recognized 55% extra circumstances than ahead tracing solely (Fig. 8a). It additionally detected 61% extra asymptomatic circumstances and averted 38% extra infections, utilizing the measure of remaining transmission potential described above. Then again, backward tracing required 78% extra contacts to be traced, 67% extra assessments and 40% extra quarantine days (Fig. 8b). Extra advantages and prices each declined for every day the contact tracing window was prolonged backwards. Though fewer circumstances have been recognized per traced contact, the decrease variety of required assessments and quarantine days result in a cost-benefit steadiness which remained beneficial relative to ahead contact tracing, relying on which price and profit measures have been thought-about (Fig. 8c).
Asympt asymptomatic. a, b present the marginal advantages and prices respectively, per day that the tracing window is prolonged backward. Each are given as a fraction of the advantages and prices of a normal ahead tracing window. c present the entire price/profit ratio of a contact tracing window prolonged to 7 days earlier than onset or take a look at, relative to a normal ahead tracing window. Combos of three price and three profit measures are proven. “Averted infectivity” denotes the variety of detected circumstances, multiplied with their remaining fraction of transmission potential in accordance with Fig. 5a. This measure of profit accounts for the remark that backward traced circumstances have been detected later of their infectious cycle. On this determine, “averted infectivity” may be thought-about equal to the variety of averted infections, with the essential caveat that it solely contains youngster circumstances of a detected case, not any subsequent averted branches of the transmission tree.